Netstat is a command-line utility that helps you monitor all the technical properties of your active network connections. It provides a quick way to see all your open ports, active connections, and network services running on your system.
If all this sounds too technical to you, don't worry; we'll explain everything simply as you read further in the article. First, let's take a look at what netstat is and how to use netstat on Windows to monitor your network.
What is the Netstat Command on Windows?
The netstat command is mainly used by IT experts or network troubleshooters on Windows and Linux systems. The command, when executed, displays a list of the active TCP connections, ports that are listening, Ethernet statistics, addresses and ports being used by your system, and more.
In simple terms, this command lets you see what network connections are active and what applications are using them in the background at any given time.
To give you clarity, below are some examples of what netstat can show you:
- All inbound and outbound connections are on your PC.
- Information about which ports are open or listening for connections.
- Connections and processes using the internet.
- Any suspicious connections from unknown applications or services.
How to Use the Netstat Command on Windows
As mentioned before, the netstat command is accessible only from the Command Prompt. If you don't know the steps, follow the ones given below to run netstat from the Command Prompt:
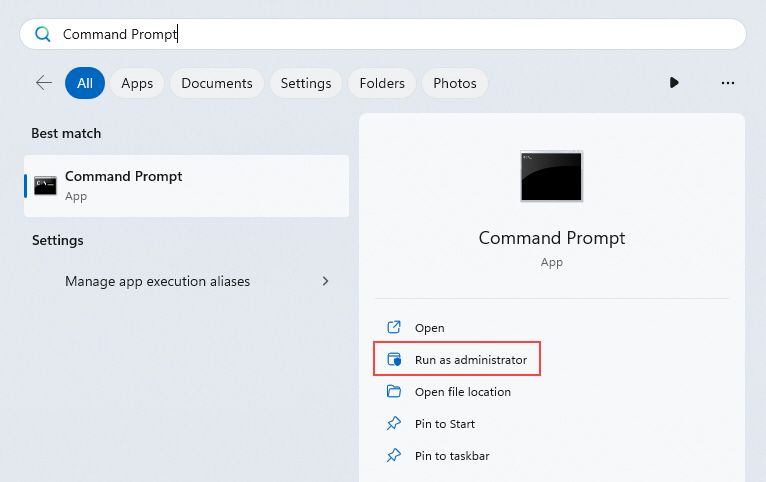
- Click on the Search button on your taskbar and search for the Command Prompt app.
- Next to the matching search result, click on Run as administrator. This will launch Command Prompt with advanced-user permissions.
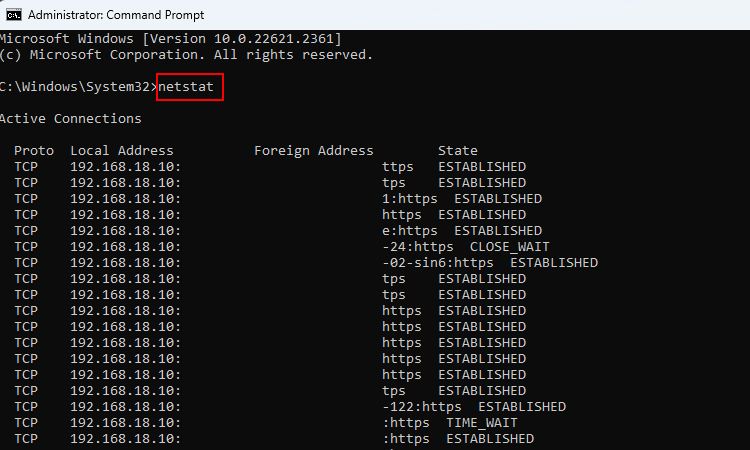
- On the Command Prompt, type netstat and press Enter. The command, after executing, will output a list of active connections along with their status.
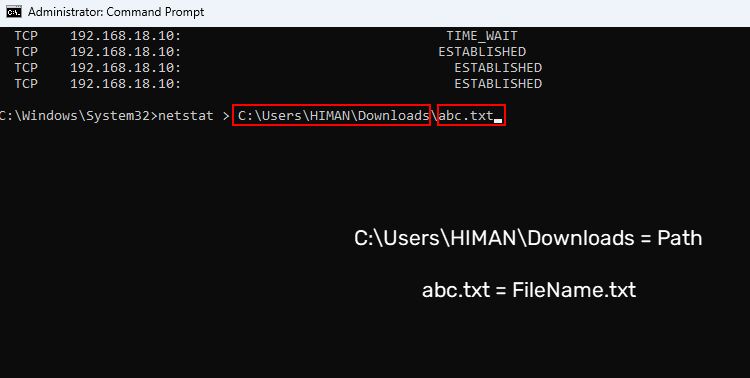
- If you need to share the output with a tech support team, for example, use this command to copy the results in a text file: "netstat > Path\FileName.txt". In this command, Path is any folder's location where you want to save the file and FileName.txt is your exported file's name.
The highlighting part of netstat is that you can further use it with some parameters (or syntaxes) to filter the generated output. We'll show you some useful parameters that you can use with the "netstat -parameter" format in the next section.
If you're eager to learn more about other such commands, check our list of useful Windows commands to manage your network.
Useful Netstat Parameters for Windows Users
In layman's terms, parameters mean some symbols or alphabets that allow you to modify what the netstat command displays. When you use a parameter with the "netstat -parameter" format, it helps you view detailed information about the traffic and different connections on a local area network.
Let's look at some useful netstat parameters to receive more specific and filtered information from netstat:
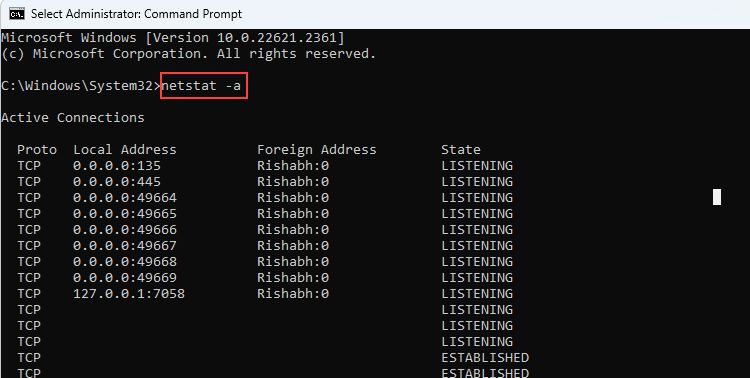
- netstat -a: It displays all the running TCP and UDP connections and the listening ports. If there are any failed connection attempts, they will be displayed here too. Besides the -a parameter, check the other alternative ways to check open TCP ports.
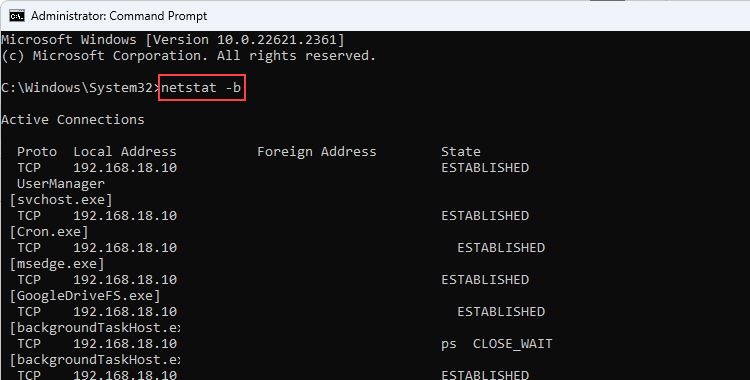
- netstat -b: The -b parameter displays the executable (.EXE) involved in creating each connection or listening port. It is mainly useful for those who deal with network troubleshooting in a Windows server or a computer part of a domain.
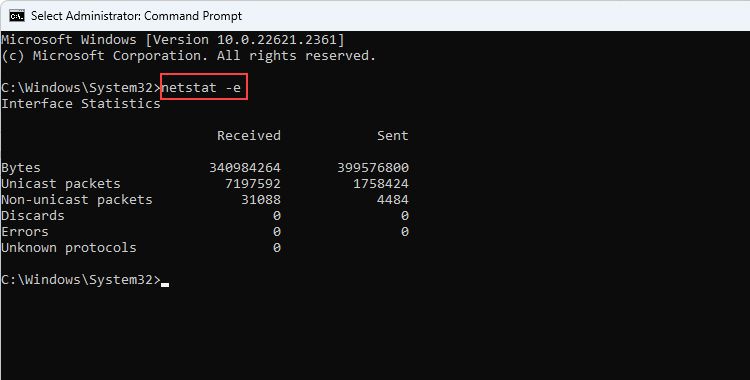
- netstat -e: If you use an Ethernet connection rather than Wi-Fi, the -e parameter can show you detailed Ethernet statistics, like link speed, total send/receive bytes, and some other technical statistics.
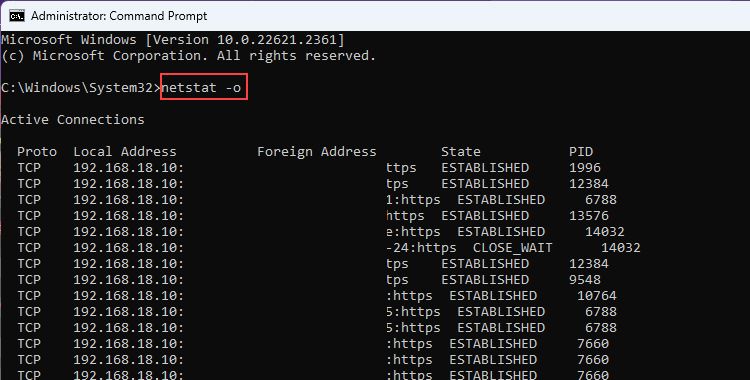
- netstat -o: Suppose you installed an application (from an untrusted website), in that case, you can check whether the application is doing something suspicious with the connection or not. This is because the -o parameter shows the Process ID (PID) of every connection that you can match from the Task Manager.
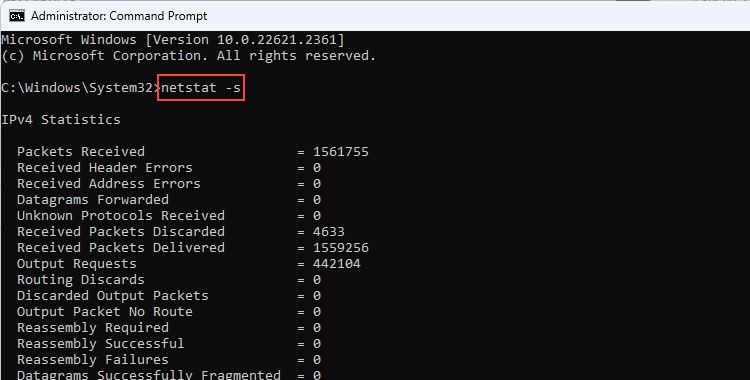
- netstat -s: This shows statistics by a protocol like packets sent/received, errors, discarded packets, etc. It's useful if you want to understand per-protocol-based bandwidth usage.
Now that you have an idea of some useful commands, try running them in the Command Prompt. Note that we recommend running Command Prompt as an administrator only as some connections are only visible with admin privileges.
If you don't like to enter the commands repeatedly, combine the parameters. For example, netstat -e -s will show you your Ethernet network details along with the per-protocol-based bandwidth usage in one view.
Above all, netstat is just one command for troubleshooting. If you're interested, check the Windows network connections tool to learn about another handy tool.
Troubleshooting Your Networks Made Easy With Netstat
Unlike utilities you need to download separately, netstat is ready to use in Command Prompt on all Windows versions. This makes it the go-to tool for getting a snapshot of network status right from your PC.
Additionally, from checking incoming and outgoing connections to sniffing out potential malicious activities, you can use it easily even if you're not a professional network expert.