Imagine having a private gossip session with your close friends or relaying sensitive information to a professional, only to find out that a nosy stranger is listening in. In the digital world, Wi-Fi eavesdropping is equivalent to these scenarios.
To protect your online privacy, it is essential to know how Wi-Fi eavesdropping works, its variations, and the best preventive measures.
How Wi-Fi Eavesdropping Attacks Work
Wi-Fi eavesdropping attacks involve intercepting and monitoring wireless network traffic without authorization. Data packets are sent over the airwaves each time you enter your password, send a message, or conduct an online transaction over a public Wi-Fi network. These packets can be intercepted by anyone with extensive Wi-Fi eavesdropping skills if they are not adequately protected.
Once an attacker has access to your data, they can analyze it to find private messages, credit card details, contact information, and passwords.
Wi-Fi eavesdropping can be carried out using numerous methods.
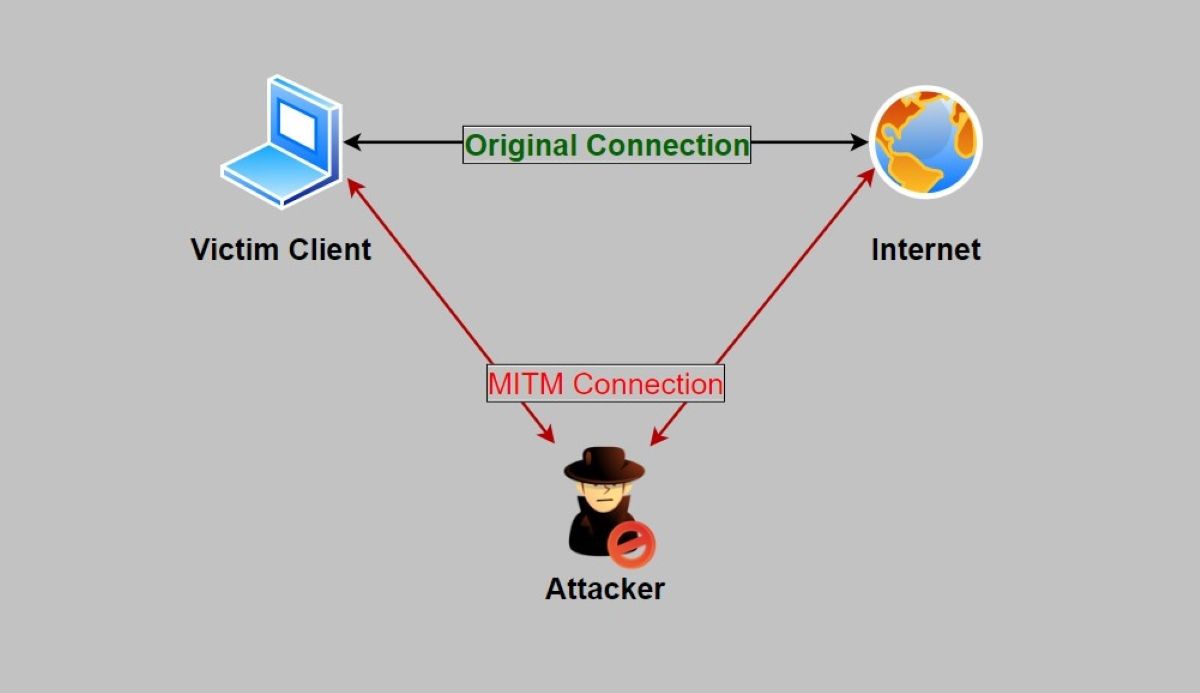
1. Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
A man-in-the-middle (MiTM) attack is where attackers intercept the data sent between two points: from your device (point A) to a service or website (point B).
In this scenario, attackers can impersonate a trusted source, often through network manipulation. This deceitful act tricks users into believing they are communicating with a legitimate entity when, in reality, they're interacting with the attacker.
By positioning themselves in the middle of the transaction or communication, the attacker can not only eavesdrop on sensitive information but also manipulate the content, potentially leading to unauthorized access, data theft, or other malicious actions.
2. Unencrypted Networks
An encrypted network safeguards your data by turning it into a secret code. Only someone with the correct key can decipher it. However, many Wi-Fi routers are set to 'unencrypted' by default.
Connecting to an unencrypted network is like laying out your personal diary in public. Scammers can easily access your web traffic and employ it for malicious activities, including MITM attacks. Sadly, with public Wi-Fi, there's no guarantee of encryption, and you can easily become a victim of Wi-Fi Eavesdropping.
3. Malware Distribution
Malware distribution refers to the methods and tactics used by cybercriminals to spread malicious software (malware) to unsuspecting users' devices.
Cybercriminals exploit software vulnerabilities and introduce malicious codes into legitimate programs. They then distribute it using various methods such as phishing, malvertising, drive-by-downloads, and more. You might unintentionally introduce the malicious software onto your system and invite Wi-Fi eavesdropping and other malign activities.
4. Malicious Hotspots
Malicious hotspots, also known as "rogue access points" or "evil twins", are Wi-Fi networks set up by cybercriminals to deceive users into thinking they are legitimate, safe networks.
Imagine connecting to what you believe is your hotel's Wi-Fi, named "XYZ Inn." Attackers set up a slight misspelling or variation, like "XYZZ Inn." Once a user is connected, the attacker can intercept data transferred between the user's device and the network. This includes websites visited, login credentials, personal information, and so on.
5. VoIP Traffic
VoIP is a technology that allows users to make voice calls using a broadband internet connection instead of a conventional or analog phone line.
Unlike traditional phone lines, which require physical access to tap into, unencrypted VoIP calls can be intercepted by anyone with access to the network who is skillful in hacking.
Since many VoIP communications traverse the open internet or shared networks, they become vulnerable targets. Attackers can intercept, record, and even manipulate VoIP calls if they are not protected.
Types of Wi-Fi Eavesdropping Attacks
There are two main types of eavesdropping attacks, each with its own techniques and potential impacts.
1. Active Attacks
In an active attack, the hacker not only intercepts the data but can also alter it before sending it back to the recipient. It's a bit like someone intercepting your mail, altering the contents, and then putting it back in the mailbox.
2. Passive Attacks
As the name suggests, passive attacks involve only "listening" without intervening. Hackers capture the data and analyze it later. Think of it as someone recording your phone call without your knowledge. Although they don't interfere with the conversation, they can still gather sensitive information.
How to Reduce the Risk of Wi-Fi Eavesdropping Attacks
You don't have to be a tech whiz to defend yourself against Wi-Fi eavesdroppers. Here are some steps to keep your data safe:
- Restrict access to sensitive information: Keep your critical transactions, like online shopping or bill payments, in a secured private network. It's acceptable to look up a café or check the weather on public Wi-Fi, but avoid handling crucial data.
- Embrace VPNs: A VPN acts as a protective tunnel for your data, shielding it from prying eyes. Investing in a reliable, paid VPN service from a trustworthy provider will bolster your security on public networks.
- HTTPS: Make sure your website, or the website you're visiting, has a URL beginning with "HTTPS" before sharing any data. This denotes an encrypted, secured site.
- Disable auto connection: Deactivate the auto-connect option on your devices. This prevents them from involuntarily seeking known networks, which can expose you to faux Wi-Fi traps set by attackers.
- Privacy screens: If you absolutely must access crucial data in public, a privacy screen ensures only you can view your screen, thwarting attempts by snoopers.
- Disable file sharing: Before connecting to public Wi-Fi, always turn off file sharing. This ensures your folders remain out of reach from anyone else on the same network.
- Use two-factor authentication (2FA): Enabling 2FA adds an additional verification layer when logging in. Even if your password is compromised on a public network, the hacker won't have the second code or verification to access your account.
- Stay updated: Regularly update your operating system. This ensures you have the latest security defenses against potential threats.
- Sign out and forget: Once done, always log out of services. Also, ensure your device forgets the network, preventing automatic reconnections.
- Use an antivirus program: Always have reliable antivirus software in place. This acts as your primary defense against common threats such as viruses and spyware.
- Connect to trusted networks only: Hackers may create fake Wi-Fi networks that look like real ones. Always double-check the network you connect to and avoid public Wi-Fi where possible.
Stay Safe From Online Eavesdropping
Using public Wi-Fi is often a convenience we can't avoid, but it can be dangerous and can lead to cyber threats. Wi-Fi eavesdropping might sound sophisticated, but you can secure yourself by using a strong password, enabling encryption, and keeping your software up to date. You should also be careful about what information you transmit over public Wi-Fi networks. With a bit of vigilance, you can enjoy your online conversations without worrying about unwanted listeners.