Your passwords are the keys to your online existence, and open the doors to your social media accounts, payment portals, perhaps even your home security system. Google's free password manager tool integrates with its other services, and allows you to access your password from any device, but how safe is it, and how does it compare to the competition?
What Is Google Password Manager?
If you've ever owned a Chromebook, an Android device, or surfed the web using Google's Chrome Browser, you've probably already come across Google password manager.
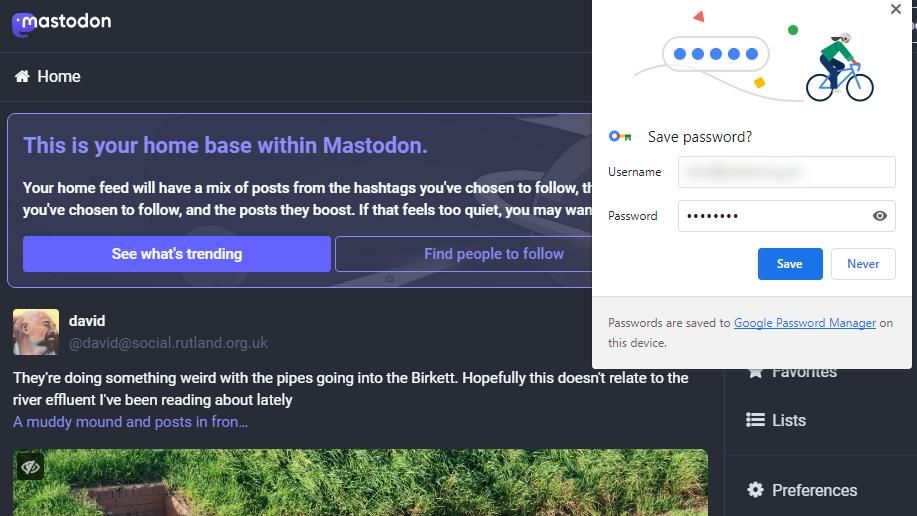
When you enter your login details on any website, you'll see a prompt, asking if you want to "Save Password". You typically have two options: "Save" and "Never".
After clicking "Save", if you visit the same website, Chrome will be able to fill in your login credentials, i.e. username and password, without you needing to remember them.
Why Should Use Google Password Manager?
In a word, simplicity. If you already use Google Chrome, it makes sense to use the integrated password tool.
You can sign in on any Chrome browser, and automatically sign into websites as if you were on your own computer.
To see saved passwords, whether or not you're logged in on Chrome or another Google device, you can visit the Google passwords domain in your browser. It's easy—you only need to remember your Google password.
Where Does Google Password Manager Store Your Passwords?
If you're logged into your Google account, your locally stored Chrome passwords will be synchronized to passwords.google.com. If you're not logged in, you can enter chrome://password-manager/passwords into the URL bar.
To access your passwords without entering a URL, you'll first need to install Google Password Manager locally. To do this, click on the menu icon in the top right of the Chrome app, and choose Install Google Password Manager..., then Install when prompted.
After this, there will be a new entry in the menu, called Google Password Manager. You can click on this to access your login credentials. Alternatively, you can click on the new icon on your desktop.
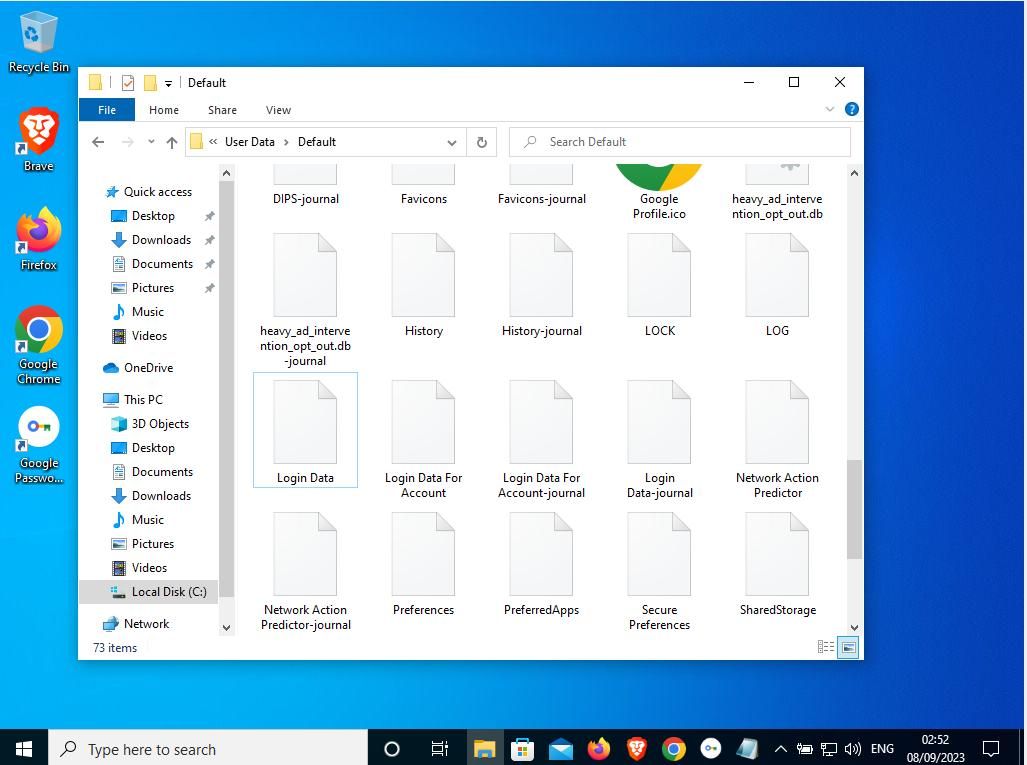
On a Windows machine, you can find your saved Google login information in an sqlite file located at C:\Users\your_username\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Login Data.
You can open this file with a dedicated Sqlite browser, or with Notepad—although if you choose the latter option, the formatting will be odd, and some characters will be unreadable.
In this file, you'll find the address of sites for which you have a saved password, your username or email address, and your encrypted password.
How Secure Is Google Password Manager?
Google is one of the largest and most powerful tech companies in the world, and if you use multifactor authentication with your Google account, the passwords and account details you store online are likely to be very safe indeed.
Google hasn't had a notable data breach since 2018, when the Wall Street Journal revealed that an API bug had been exposing private data for more than three years. This data did not, however, include passwords.
Google Password Manager's main vulnerability lies on your PC, and there are two ways that attackers could gain access to your account.
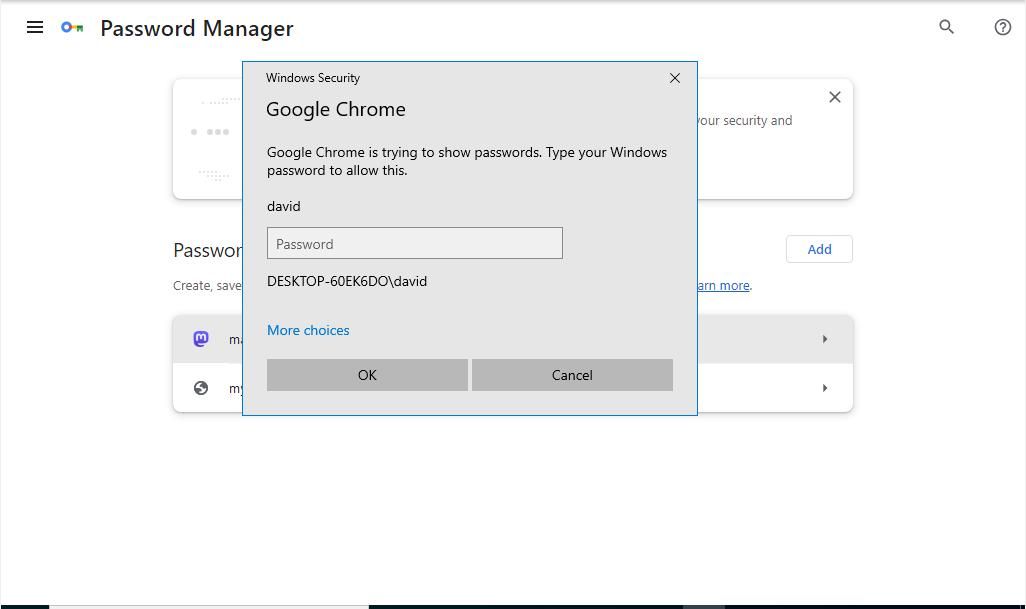
The first is to open the password manager app. The attacker would require physical access to your machine in order to do this, and would likely be foiled when asked to enter your system password. If they manage to crack your system password, they would then be able download all of your logins and passwords without encryption.
The second potential problem is the database file.
To compromise an account, an attacker needs to know three things: that an account exists with a particular service, the username associated with the account, and the password.
In the database file on your PC, these first two factors are in plain text, and only the password is encrypted. If an attacker manages to copy this away from your PC, it can be cracked at their leisure. Lists of passwords associated with usernames and services are also available in online marketplaces. You can check if credentials have been compromised at haveibeenpwned.
Actually getting hold of the file isn't difficult if an attacker has access to the machine, and we timed ourselves exfiltrating it on a USB stick in mere seconds. Alternatively, email will do.
Attackers may also try to put malware onto your PC in order to steal the file.
Are Dedicated Online Password Managers Safer Than Google Password Manager?
Online password managers are a growing industry, and store all of your passwords in an encrypted vault, and encourage the use of strong, randomly generated passwords. These vaults are typically secured by a master password.
While this may seem like a secure solution, the 2022 LastPass data breach demonstrated that it's possible for sophisticated attackers to download password vaults, and encryption keys—giving them easy access to all of your accounts and data. Very little is actually uncrackable, so there are risks, however slight, no matter your storage method.
There's No Best Solution for Safe Password Management
Usernames and passwords are an important target for criminals, and it's important to keep yours safe and secure. But no password management system is entirely safe from attack. One possible solution is to use stateless password managers that generate passwords for sites based on a number of parameters including the login URL your email address, and a secret phrase.